Size in Square Kilometres
39255
Qualifying Species and Criteria
Criterion D(2) – Marine Mammal Diversity
Criterion D (2) – Marine Mammal Diversity
Arctocephalus forsteri, Balaenoptera borealis, Balaenoptera edeni, Balaenoptera musculus, Balaenoptera physalus, Caperea marginata, Cephalorhynchus hectori, Delphinus delphis, Eubalaena australis, Globicephala macrorhynchus, Globicephala melas, Hydrurga leptonyx, Kogia breviceps, Lissodelphis peronii, Megaptera novaeangliae, Mesoplodon densirostris, Mesoplodon grayi, Mesoplodon layardii, Mirounga leonina, Orcinus orca, Physeter macrocephalus, Stenella coeruleoalba, Tursiops truncatus, Ziphius cavirostris
Other Marine Mammal Species Documented
Summary
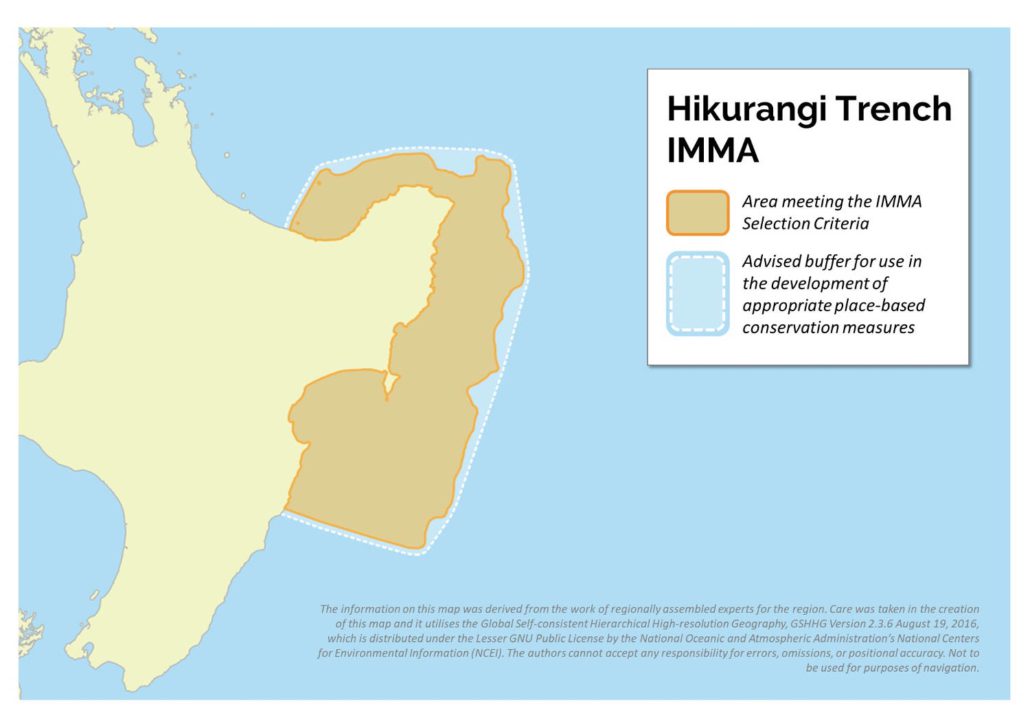
The Hikurangi Trench lies parallel to the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand. This IMMA starts from southern Hawke’s Bay to about 100km offshore up to East Cape and shallower slope and shelf areas from East Cape to Whakatane, eastern Bay of Plenty. The Hikurangi Trench is a southerly extension of the Kermadec Trench incorporating a highly diverse canyon and channel system. The westward extension of the IMMA into the eastern part of the Bay of Plenty provides an important corridor connecting the two systems. The area is important to pygmy sperm whales (Kogia breviceps), accounting for 65% of all New Zealand strandings, including a high proportion of mother/calf pairs. The canyon systems support an exceptional diversity of deep diving-cetaceans, various inshore delphinids and New Zealand fur seals (Arctocephalus forsteri) over the shelf.
Description of Qualifying Criteria
Criterion A – Species or Population Vulnerability
Criterion B – Distribution and Abundance
Sub-criterion B1 – Small and Resident Populations
Sub-criterion B2 – Aggregations
Criterion C: Key Life Cycle Activities
Sub-criterion C1 – Reproductive Areas
Sub-criterion C2: Feeding Areas
Sub-criterion C3: Migration Routes
C3a – Whale Seasonal Migratory Route
C3b – Migration / Movement Area
Criterion D – Special Attributes
Sub-criterion D1 – Distinctiveness
Sub-criterion D2 – Diversity
Limited sightings data and the stranding record indicate the occurrence of 22 cetacean and 3 pinniped species in this IMMA (Brabyn 1991, Baird 2011, New Zealand Department of Conservation (DOC) Marine Mammal Sighting and Stranding database 2020). This represents an exceptional diversity of deep diving cetaceans. There is also a high diversity of other cetaceans including coastal and shelf delphinids (including killer whales, common dolphins, striped dolphin and Hector’s dolphin), and mysticetes including 6 rorqual species, the southern right whale, and the pygmy right whale (Brabyn 1991, Baker and van Helden 1999, Baker 2002, van Helden et al 2002,Thompson et al 2013, Gaskin 1973, Roberts et al 2019, Freeman 2003, Betty et al. 2020, Cranswick et al. 2022, DOC Marine Mammal Sighting and Stranding database 2020). The primary species recorded for the region are pygmy sperm whale, Gray’s beaked whale, strap-toothed beaked whale, and Cuvier’s beaked whale (Baker and van Helden 1990, Thompson et al. 2013). There are numerous records of strandings and sightings of various species of Balaenopteridae (Dawbin 1956, DOC Marine Mammal Sighting and Stranding database 2020). Sighting records of southern right whales are increasing (Cranswick et al. 2022). New Zealand fur seals are common in the region with 2 other pinniped species (i.e. southern elephant seal, leopard seal) regularly recorded from the region. The warm subtropical East Cape Current may explain the occasional records of cetaceans more commonly sighted in tropical waters (e.g. short-finned pilot whale, dense beaked whale).
Supporting Information
Baird, S.J. 2011. New Zealand fur seals – summary of current knowledge. New Zealand Aquatic Environment and Biodiversity Report No. 72. 51 p.
Baker, A.N. 2002. ‘Status, relationships, and distribution of Mesoplodon bowdoini Andrews, 1908 (Cetacea: Ziphiidae)’. Marine Mammal Science 17: 473-493.
Baker, A.N. and van Helden, A.L. 1990. ‘First record of the dwarf sperm whale, Kogia simus (Owen), from New Zealand. National Museum of New Zealand Records’ 3: 125-130.
Baker, A.N. and van Helden, A.L. 1999. ‘New records of beaked whales, Genus Mesoplodon, from New Zealand (Cetacea: Ziphiidae).’ Journal of The Royal Society New Zealand 29: 235-244
Beatson, E. 2007. ‘The diet of pygmy sperm whales, Kogia breviceps, stranded in New Zealand: implications for conservation’. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 17:295–303 DOI 10.1007/s11160-007-9039-9
Betty, E.L., Bollard, B., Murphy, S., Ogle, M., Hendriks, H., Orams, M.B., Stockin, K.A. 2020. ‘Using emerging hot spot analysis of stranding records to inform conservation management of a data-poor cetacean species’. Biodiversity and Conservation 29: 643-665
Brabyn, M. 1991. An analysis of the New Zealand Whale Stranding record. Science and Research Series No. 29. Department of Conservation, Wellington.
Carroll, E.L., Rayment, W.J., Alexander, A.M., Baker, C.S., Patenaude, N.J., Steel, D., Constantine, R., Cole, R., Boren, L., and Childerhouse, S. 2014. ‘Reestablishment of former wintering grounds by New Zealand southern right whales’. Marine Mammal Science 30: 206-220
Cranswick, A.S.,Constantine, R., Hendricks, H., Carroll, E.L. 2022. Social media and citizen science records are important for the management of rarely sighted whales. Ocean & Coastal Management 226: 106271
Dawbin, W.H. 1956. ‘The migrations of humpback whales which pass the New Zealand coast’. Transactions and Proceedings of the Royal Society of New Zealand 84: 147-196
Freeman, D. 2003. A review of records of Hector’s dolphin (Cephalorhynchus hectori) from the East Cast of the North Island, New Zealand. Department of Conservation Technical Support Series No 11. Department of Conservation, Gisborne, New Zealand.
Gaskin, D. E. 1968. Distribution of Delphinidae (Cetacea) in relation to sea surface temperatures off Eastern and Southern New Zealand. ‘New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 2: 527-534
Gaskin, D.E. 1973. ‘Sperm whales in the western South Pacific’, New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 7: 1-20, DOI: 10.1080/00288330.1973.9515453
Hadfield, M.G., Rickard, G.J., and Uddstrom, M.J. 2007. ‘A hydrodynamic model of Chatham Rise, New Zealand’. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 41: 239-264, DOI: 10.1080/00288330709509912
Roberts, J.O., Webber, D.N., Roe, W.D., Edwards, C.T.T., and Doonan, I.J. 2019. Spatial risk assessment of threats to Hector’s and Māui dolphins (Cephalorhynchus hectori). New Zealand Aquatic Environment and Biodiversity Report No. 214. Fisheries New Zealand, Wellington, New Zealand, pp. 168
Riekkola, L., Zerbini, A.N., Andrews, O., Andrews-Goff, V., Baker, C.S., Chandler, D., Childerhouse, S., Clapham, P., Dodemont, R., Donnelly, D., Friedlaender, A., Gallego, R., Garrigue, C., Ivashchenko, Y., Jarman, S., Lindsay, R., Pallin, L., Robbins, J., Steel, D., Tremlett, J., Vindenes, S., and Constantine, R. 2018. ‘Application of a multi-disciplinary approach to reveal population structure and Southern Ocean feeding grounds of humpback whales’. Ecological Indicators 89: 455-465
Thompson, K., Baker, C.S., van Helden, A., Patel, S., Millar, C., and Constantine, R., 2012. ‘The world’s rarest whale’. Current Biology 22: R905–906.
Thompson, K.F., Millar, C.D., Baker, C.S., Dalebout, M., Steel, D., van Helden, A.L., and Constantine, R. 2013. ‘A novel approach provides insights into the management of rare cetaceans’. Biological Conservation 157: 331-340
van Helden, A.L., Baker, A.N., Dalebout, M.L., Reyes, J.C., Van Waerebeek, K., and Baker, C.S. 2002. ‘Resurrection of Mesoplodon traversii (Gray, 1874), senior synonym of M. bahamondi Reyes, Van Waerebeek, Cárdenas and Yáñez, 1995 (Cetacea: Ziphiidae)’. Marine Mammal Science 18: 609–621
New Zealand Department of Conservation (DOC) 2020. Marine Mammal Sighting and Stranding database. Public database maintained by DOC on behalf of New Zealand Government. Available from marinemammals@doct.govt.nz. Accessed in June 2020.
Downloads
Download the full account of the Hikurangi Trench IMMA using the Brochure button below:
To make a request to download the GIS Layer (geopackage and/or geojson) for the Hikurangi Trench IMMA please complete the following Contact Form: